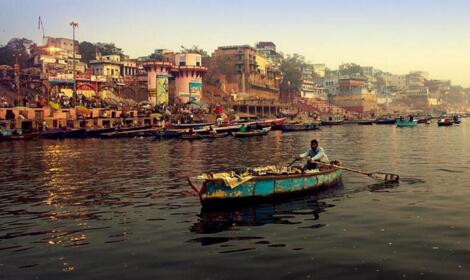你对印度河流域文明了解多少?
正文翻译
The Indus Valley Civilization was known for its impressive cities and infrastructure, including well-planned streets, advanced drainage systems, and complex water management techniques. Their cities, such as Harappa and Mohenjo-Daro, were some of the largest of the ancient world.
印度河谷文明以其令人惊叹的城市和基础设施而闻名,包括规划良好的街道、先进的排水系统和复杂的水管理技术。他们的城市,如哈拉帕和摩亨佐-达罗,是古代世界上最大的城市之一。
印度河谷文明以其令人惊叹的城市和基础设施而闻名,包括规划良好的街道、先进的排水系统和复杂的水管理技术。他们的城市,如哈拉帕和摩亨佐-达罗,是古代世界上最大的城市之一。
评论翻译
Jeevanandham
Related :What is the Indus Valley civilization?
Short answer about Indus Valley Civilization which i know.
In history, there were four major civilization namely
Mesopotamian
Chinese,
Egyptian
Indus Valley Civilization
Out of which, Indus Valley Civilization is the largest in largest in terms of its area(1,260,000 square kilometres). It was spread over India, Pakistan, Afghanistan etc. Current findings scientists show that the extent of the civilization was even bigger.
关于印度河流域文明的简短回答,根据我所知道的,历史上有四个重要的文明,分别是美索不达米亚、中国、埃及和印度河流域文明。其中,印度河流域文明在面积上是最大的(1,260,000平方公里),它分布在印度、巴基斯坦、阿富汗等地。目前,科学家的研究表明,这个文明的范围甚至更大。
It had Ghagra-Hakra valley to the east, Makran Coast (Baluchistan) to the west, Afghanistan in northeast and Daimabad (Maharashtra) in south.
During its peak, it had a population of 5 million (This is greater than present day population of New Zealand. Most of its inhabitants were artisans and traders.). Out of the 5 million people, many of them lived in villages. archaeologists are having tough time finding culture and society in which they lived because of absence of any proper evidence. Their residences, were made of mud or wood which gets damaged easily and hence no trace is available.
Due to its vast area, 1056 cities have been found. Out of these 1056 cities, 96 of them have been excavated. Dholavaria, Rakhigarhi, Lothal, Kalibangan are some of the famous urban cities apart from Harappa and Mohenjo-Daro.
印度河流域文明的东部有格拉格拉-哈克拉谷,西部有马卡兰海岸(俾路支省),东北部为阿富汗,南部为戴马巴德(马哈拉施特拉邦)。
在其鼎盛时期,该文明有500万人口(这比新西兰现今的人口还多)。大多数居民是手工艺人和商人,而其中许多人住在村庄里。考古学家很难找到他们所生活的文化和社会,因为没有任何确切的证据。他们的住所主要是由泥土或木材建造而成,很容易被损坏,因此没有任何痕迹留下。
由于其广阔的领域,已经发现了1056个城市。其中96个城市已经被挖掘出来。多哈拉维拉、拉基加里、洛塔尔、卡利班甘等著名城市除了哈拉帕和摩亨佐-达罗之外。
Harappans are famous for their world-class drainage system. The usage of flush toilets, removal of waste water, channelling fresh water into bathrooms – they were masters in this area.
Town planning was not limited to cities alone, every town, village and city had the same grid pattern and every house constructed used the same bricks, which were of a particular dimension. The bricks were same for all the houses.
哈拉帕人以他们世界级的排水系统而闻名。使用冲水马桶、排放废水,将清洁的水引入浴室——在这个领域他们是专家。
城镇规划不仅仅局限于城市,每个城镇、村庄和城市都有相同的网格图案,每个建筑所使用的砖块尺寸也相同。这些砖块对于所有房屋来说都是一样的。

Another interesting thing in Indus Valley Civilization is till date there is no evidences of any authority or leader ruling this civilization.
In Lothal, one of the cities of the Civilization, water transport means were available and aquaculture was practised.
These cities had spacious roads. Mohenjo-Daro roads were 10 metres wide and the smallest roads width is estimated to be at least 1.5 m-3m.
The houses used burnt bricks and every house had the same planning (construction) but the rich people had 3 storied houses while the normal ones had 2 storied houses. Those houses had courtyards and terraces too.
印度河流域文明中另一个有趣的事情是,到目前为止没有证据表明有任何权威或领袖统治着这个文明。
在这个文明的一个城市洛塔尔,水运输工具得到了应用,也进行了水产养殖。
这些城市有宽敞的道路。摩亨佐-达罗的道路宽度为10米,最小的道路宽度估计至少为1.5米-3米。
这些房屋使用烧制砖块建造,每个房屋的规划(建设)都相同,但是富人有三层的房子,普通人则有两层的房子。这些房子还有庭院和露台。

Harappa was the first city to be discovered and it was discovered by Dayaram Sahni in 1921. Its present location is in Punjab (Pakistan). It was present on the banks of River Ravi.
The second city to be discovered was Mohenjo-Daro. It was discovered by R.D. Banerjee. Its present location is in Sindh (Pakistan). It was present on the banks of River Indus.The word Mohenjo-Daro literally meant the “mound of dead”.
In Lothal (Gujarat), ruins of dockyard were excavated. Rice was cultivated there and there was a game similar to Chess. People of Indus Valley Civilization traded with Mesopotamian Civilization from there.
哈拉帕是被发现的第一个城市,由达亚拉姆·萨赫尼于1921年发现。它现在位于旁遮普邦(巴基斯坦)。它位于拉维河畔。
第二个被发现的城市是摩亨佐-达罗。它由R.D.班纳吉发现,现在位于信德省(巴基斯坦)。它位于印度河畔。Mohenjo-Daro这个词的字面意思是“死者之丘”。
在古吉拉特邦的洛塔尔,码头的废墟被挖掘出来。在那里种植了大米,还有一种类似于国际象棋的游戏。印度河流域文明人从那里与美索不达米亚文明进行贸易。

In a city called Chanduraho (Indus), evidences of cosmetics were found. Women used lipsticks and other cosmetics. Even small dressing tables were found.
Lets some of their position in early periods.
They were the world’s first dentists.
Earliest scale to test purity of Gold.
The first people to domesticate Cotton.
Indus Valley Civilization people invented the world’s first buttons.
They made the world’s oldest signboard
Another astonishing fact about Induc Valley Civilization is that has surprised the researchers is the absence of any structure which can be thought of central importance like a palace or a temple. The presence of a temple or a palace is a standard feature of every other early civilization. There are several public buildings like the Great Baths and granaries but no structure can be even remotely related to a palace or temple. This has made some scholars to believe that Indus Valley cities were an egalitarian society.
egalitarian means all people are equal.
Yes that’s all i know about Indus Valley Civilization if i get to know anything interesting about Indus Valley Civilization i will upxe.
The best quote which suits for Indus Valley Civilization.
“Civilizations are not remembered by their business people, their bankers or lawyers. They''re remembered by the arts.” - Eli Broad
UPVOTE GUYS IF YOU LIKE MY ANSWER.
THANK YOU!!!
在一个名为钱杜拉霍(印度河流域)的城市,发现了化妆品的证据。女性使用口红和其他化妆品。甚至还发现了小化妆台。
让我们回顾一下他们在早期的一些成就:
他们是世界上第一个牙医。
使用最早的黄金纯度测试比例尺。
第一个驯养棉花的人类。
印度河流域文明人发明了世界上第一个纽扣。
他们制造了世界上最古老的招牌。
印度河流域文明中另一个令研究者惊异的事实是缺乏任何被认为具有中心重要性的结构,如宫殿或寺庙。寺庙或宫殿的存在是每个其他早期文明的标准特征。有若干公共建筑,如巨大的浴池和粮仓,但是没有任何结构与宫殿或寺庙有任何关联。这促使一些学者认为,印度河流域城市是一个平等主义的社会。
平等主义意味着所有人都是平等的。
这是我所知道的关于印度河流域文明的所有内容。如果我了解到关于印度河流域文明的任何有趣信息,我会进行更新。
以下是适用于印度河流域文明的最佳引语:
“文明不是因为他们的商人、银行家或律师而被人们记忆,而是因为他们的艺术。”- Eli Broad
如果您喜欢我的回答,请点赞。谢谢!
All About
= Indus civilization is one of the four earliest civilization of the world along with the civilization of mesopotamia ( tigeris and Euphrates) Egypt (nile) and china ( Hwang Ho ).
= The civilization froms part of the proto-history of india and belong to the Bronze age.
= The most accepted periods is 2500-1700 Bc (by carbon 14 dating).
= Dyaram sahani first discovered harapa in 1921.
= RD Benerjee discovered Mohenjodaro or Mound the dead in1922.
Town planning and structure
= Town planing was not uniform. A common feature was grid systems Street cutting across one another at Right angle, dividing the Town into large rectangle blocks.
= The towns were divided into parts,uper part or lower part.
= Underground drainage system connected all house to the street drains made of moter ,lime and gypsum.They were covered with either brick or stone slabs and equipped with manhole. This shows developed senseof health and sanitation.
= The great Bath it was used for religious bathing. Steps at either end lead to the surface. With inlet to the tank and outlet to drain water . There were changing rooms alongside.
= The Granaries (Harappa)6 granaries in a row were found in the citadel Harappa.
= House were made up of burnt bricks ..
= Lampeter were erected at regular intervals. It indicates the existence of Street lighting.
sonmaninath.blogspot.com
●印度河流域文明是世界上最早的四个文明之一,与美索不达米亚文明(底格里斯和幼发拉底河)、埃及文明(尼罗河)和中国文明(黄河)并列。
●该文明是印度原始史的一部分,属于青铜时代。
●最被接受的时间是公元前2500-1700年(通过碳14测年)。
●Dyaram Sahani于1921年首次发现了哈拉帕。
●RD Benerjee于1922年发现了死人堆或摩亨佐达罗。
城镇规划和结构:
●城镇规划不统一。一个常见特点是网格系统,街道相互交叉成直角,将城镇划分为大矩形区块。
●城镇被划分为上部或下部。
●地下排水系统将所有房屋连接到由灰泥、石灰和石膏制成的街道排水沟。它们覆盖有砖或石板,并配有检修口。这表明他们具有发展健康和卫生意识。
●大浴池是用于宗教沐浴的。两端的台阶通向水面。有进水口和排水口。旁边设有更衣室。
●粮仓(哈拉帕)在城堡哈拉帕发现了6个粮仓。
●房屋由烧制的砖块建造而成。
●灯柱定期竖立。这表明存在街道照明。
来源:http://sonmaninath.blogspot.com/
Sathya Sathesh
By 2600 BCE, small Early Harappan communities had developed into large urban centers. These cities include Harappa, Ganeriwala, and Mohenjo-daro in modern-day Pakistan and Dholavira, Kalibangan, Rakhigarhi, Rupar, and Lothal in modern-day India. In total, more than 1,052 cities and settlements have been found, mainly in the general region of the Indus River and its tributaries.
Mohenjo-daro is thought to have been built in the twenty-sixth century BCE; it became not only the largest city of the Indus Valley Civilization but one of the world’s earliest major urban centers. Located west of the Indus River in the Larkana District, Mohenjo-daro was one of the most sophisticated cities of the period, with advanced engineering and urban planning.
到公元前2600年,小规模的早期哈拉帕社区已经发展成了大型城市中心。这些城市包括今天巴基斯坦的哈拉帕、甘尼隆瓦拉和摩亨佐达罗,以及今天印度的多拉维拉、卡利班甘、拉克希加尔希、鲁帕尔和洛塔尔等。总共发现了1,052个城市和定居点,主要位于印度河及其支流的一般地区。
摩亨佐达罗被认为是建造于公元前26世纪;它不仅成为印度河谷文明最大的城市之一,而且也是世界上最早的重要城市之一。位于拉尔卡纳区的印度河西岸,摩亨佐达罗是该时期最复杂的城市之一,具有先进的工程和城市规划。

Harappa was a fortified city in modern-day Pakistan that is believed to have been home to as many as 23,500 residents living in sculpted houses with flat roofs made of red sand and clay. The city spread over 150 hectares—370 acres—and had fortified administrative and religious centers of the same type used in Mohenjo-daro.
Both cities had similar organization and featured citadels, central areas in a city that were heavily fortified—protected with defensive military structures. Additionally, both cities were situated along the Indus River. This structure would have allowed those at the higher levels of the buildings in either city to look down the river and see into the distance.
哈拉帕是位于今天巴基斯坦的一座有防御工事的城市,据信曾经是居住着多达23,500名居民的地方,他们生活在由红色沙土和黏土制成的雕刻房屋中,并拥有平屋顶。该城市占地150公顷(370英亩),并拥有与摩亨佐达罗相同类型的设有防御措施的行政和宗教中心。
两个城市具有相似的组织结构和特点,都有城堡,即城市中被大量加固、用防御性军事结构保护的中心区域。此外,两个城市都位于印度河沿岸。这种结构使得任一城市楼房处于较高位置的人能够俯瞰河流并看到远处的情况。
The remains of the Indus Valley Civilization cities indicate remarkable organization; there were well-ordered wastewater drainage and trash collection systems and possibly even public baths and granaries, which are storehouses for grain. Most city-dwellers were artisans and merchants grouped together in distinct neighborhoods. The quality of urban planning suggests efficient municipal governments that placed a high priority on hygiene or religious ritual.
Harappans demonstrated advanced architecture with dockyards, granaries, warehouses, brick platforms, and protective walls. These massive walls likely protected the Harappans from floods and may have deterred military conflicts. Unlike Mesopotamia and Ancient Egypt, the inhabitants of the Indus Valley Civilization did not build large, monumental structures. There is no conclusive evidence of palaces or temples—or even of kings, armies, or priests—and the largest structures may be granaries. The city of Mohenjo-daro contains the Great Bath, which may have been a large, public bathing and social area.
印度河流域文明城市的遗迹表明,这个文明的组织极为完善;城市内有井然有序的废水排放和垃圾收集系统,甚至可能还有公共浴室和粮仓,用于储存谷物。大多数城市居民是手工艺人和商人,聚居在不同的社区中。高质量的城市规划意味着高效的市政府,非常注重卫生或者宗教仪式。哈拉帕人展示了先进的建筑技术,包括船坞、粮仓、仓库、砖块平台和保护墙等。这些巨大的墙壁很可能保护哈拉帕人免受洪水袭击,也可能阻止了军事冲突。与两河流域和古埃及不同,印度河流域文明的居民没有建造大规模的纪念性建筑。没有确凿的证据可以证明有宫殿或寺庙,也没有国王、军队或祭司的存在,最大的建筑物可能是粮仓。摩亨佐达罗市包含了一个名为“大浴池”的建筑,可能是一个大型的公共浴场和社交区域。

The people of the Indus River Valley Civilization achieved many notable advances in technology, including great accuracy in their systems and tools for measuring length and mass. Fire-baked bricks—which were uniform in size and moisture-resistant—were important in building baths and sewage structures and are evidence that Harappans were among the first to develop a system of standardized weights and measures. The consistency of brick size across cities also suggests unity across the various urban areas, which is evidence of a broader civilization.
印度河流域文明的人民在技术方面取得了许多显著进展,其中包括他们用于测量长度和质量的系统和工具的高度准确性。经火烤制的砖头是建造浴池和污水结构的重要材料,它们尺寸统一、防潮,也是哈拉帕人最早开发出标准化重量和度量系统的证据之一。不同城市中砖头尺寸的一致性也表明了不同城市之间的统一,这是一个更广泛的文明的证据。

Harappa, Mohenjo-daro, and the recently partially-excavated Rakhigarhi demonstrate the world's first known urban sanitation systems. The ancient Indus systems of sewage and drainage developed and used in cities throughout the Indus region were far more advanced than any found in contemporary urban sites in the Middle East and even more efficient than those in many areas of Pakistan and India today. Individual homes drew water from wells, while wastewater was directed to covered drains on the main streets. Houses opened only to inner courtyards and smaller lanes, and even the smallest homes on the city outskirts were believed to have been connected to the system, further supporting the conclusion that cleanliness was a matter of great importance.
哈拉巴、摩亨佐达罗以及最近部分挖掘的拉基加里展示了世界上已知的第一个城市卫生系统。古印度河流域地区在各个城市中开发和使用的污水和排水系统比现代中东地区的任何城市都要先进得多,甚至比今天巴基斯坦和印度许多地区的城市卫生系统更有效。每户人家都从井中取水,而废水则被引导到主要街道上的覆盖排水沟中。房屋只对内部庭院和小巷开放。即使是城市郊区的最小住宅也被认为与该系统相连,这进一步支持了清洁卫生对于哈拉巴文明来说是非常重要的结论。
Harappans are known for seal carving— the cutting of patterns into the bottom face of a seal, a small, carved obxt used for stamping. They used these distinctive seals for the identification of property and to stamp clay on trade goods. Seals—decorated with animal figures, such as elephants, tigers, and water buffalos—have been one of the most commonly discovered artifacts in Indus Valley cities.
The Indus River Valley Civilization is considered a Bronze Age society; inhabitants of the ancient Indus River Valley developed new techniques in metallurgy—the science of working with copper, bronze, lead, and tin. Harappans also performed intricate handicraft using products made of the semi-precious gemstone Carnelian.
哈拉巴人以刻印章而闻名——在印章的底部刻图案,这是一种小型雕刻物件,用于盖章。他们使用这些独特的印章来识别财产和盖印贸易商品上的黏土。装饰有动物形象(如象、老虎和水牛)的印章是印度河谷城市中最常见的文物之一。
印度河流域文明被认为是青铜时代社会;古印度河谷居民在冶金学领域—即利用铜、青铜、铅和锡进行加工的科学方面开发出新技术。哈拉巴人还使用半宝玉石玛瑙制作精细的手工艺品。

Evidence shows Harappans participated in a vast maritime—sea—trade network extending from Central Asia to the Middle East. The civilization's economy appears to have depended significantly on trade, which was facilitated by major advances in transport technology. The Harappan Civilization may have been the first to use wheeled transport, in the form of oxcarts that are identical to those seen throughout South Asia today. It also appears they built boats and watercraft—a claim supported by archaeological discoveries of a massive, dredged canal, and what is regarded as a docking facility at the coastal city of Lothal. Harappans also engaged in shellworking, and shells used in their crafts have origins from as far away as the coast of modern-day Oman.
证据表明,哈拉巴人参与了从中亚到中东延伸的广泛海上贸易网络。该文明的经济似乎在很大程度上依赖于贸易,而前进的运输技术也促进了这一过程。哈拉巴文明可能是第一个使用车轮运输形式的文明,他们使用耕牛车,这种车辆现在在整个南亚都可以看到。此外,他们还建造了船只和水上交通工具——这一说法得到了考古发现的支持,例如在海滨城市洛塔尔发现的巨大的疏浚运河和被认为是停泊设施的遗址。哈拉巴人还从事贝壳工艺,并且用于其手工艺品中的贝壳来自今天阿曼海岸远至万里之外的地方。
The Indus Valley Civilization declined around 1800 BCE, and scholars debate which factors resulted in the civilization’s demise. One theory suggested that a nomadic, Indo-European tribe called the Aryans invaded and conquered the Indus Valley Civilization, though more recent evidence tends to contradict this claim. Many scholars believe that the collapse of the Indus Valley Civilization was caused by climate change. Some experts believe the drying of the Saraswati River, which began around 1900 BCE, was the main cause for climate change, while others conclude that a great flood struck the area.
印度河谷文明在公元前1800年左右衰落,学者们争论导致这一文明灭亡的因素。一种理论认为,一个名为雅利安人的游牧印欧部落入侵并征服了印度河谷文明,但更近期的证据倾向于否定这一说法。许多学者认为,印度河谷文明的崩溃是由于气候变化引起的。一些专家认为,始于公元前1900年左右的萨拉斯瓦蒂河干涸是气候变化的主要原因,而另一些人则得出结论称该地区遭受了一场大洪水的袭击。
Various elements of the Indus Civilization are found in later cultures, suggesting the civilization did not disappear suddenly due to an invasion. Many scholars argue that changes in river patterns caused the large civilization to break up into smaller communities called late Harappan cultures.Another disastrous change in the Harappan climate might have been eastward-moving monsoons, or winds that bring heavy rains. Monsoons can be both helpful and detrimental to a climate, depending on whether they support or destroy vegetation and agriculture.
后来的文化中发现了印度文明的各种元素,这表明这个文明并没有因为入侵而突然消失。许多学者认为,河流模式的变化导致了大的文明分裂成称为晚期哈拉帕文化的小社区。
哈拉巴气候的另一个灾难性变化可能是向东移动的季风或带来暴雨的风。季风对气候既有益处也有不利之处,这取决于它们是否支持或破坏植被和农业。
By 1800 BCE, the Indus Valley climate grew cooler and drier, and a tectonic event may have diverted or disrupted river systems, which were the lifelines of the Indus Valley Civilization. The Harappans may have migrated toward the Ganges basin in the east, where they could have established villages and isolated farms. These small communities would not have been able to produce the same agricultural surpluses to support large cities. With the reduced production of goods, there would have been a decline in trade with Egypt and Mesopotamia. By around 1700 BCE, most of the Indus Valley Civilization cities had been abandoned.
公元前1800年,印度河谷气候变得更加凉爽和干燥,构造事件可能改道或破坏了河系,而这些河系是印度河谷文明的命脉。哈拉巴人可能向东迁徙到恒河流域,在那里他们可以建立村庄和孤立的农场。这些小社区不可能生产出支持大城市的同样的农业剩余物。随着商品生产的减少,与埃及和美索不达米亚的贸易也将下降。到公元前1700年左右,大多数印度河谷文明城市已经被遗弃了。
The sheer age of the IVC should be interesting to most ordinary people anyway.
So what are the reasons for this neglect??
Some part of neglect is probably due to the Indus scxt being not deciphered till now. Yet, it can be argued that the Linear A scxt is also not deciphered and the culture is still analysed more than IVC.
Does bias and discrimination play the most part here? Is it because that most historians grew up in a Western culture and Western culture shared ideas from the Greek and Roman. So they identified themselves or their ancestors more with the Greek and Roman and so they are more interested in them than IVC?
Or are there any other reasons?
What is the near-term forecast? Will analysis of IVC grow over over a few years or will it remain the same?
印度河谷文明的悠久历史本应引起大多数普通人的兴趣。那么,为什么它会被忽视呢?
部分原因可能是因为迄今为止尚未解读印度文字。然而,可以说线性A文字也没有被解读,但该文化仍然比印度河谷文明被更多地分析。这里是否存在偏见和歧视的因素?是不是因为大多数历史学家在西方文化中成长,并且西方文化分享了希腊和罗马的思想。所以他们对希腊和罗马或者与之有关的先祖更感兴趣,而对印度河谷文明则不太感兴趣?
还是有其他原因吗?未来一段时间内,印度河谷文明的分析会增加还是保持不变?
Trishala
When you travel back to the beginning of civilization on earth, all the civilizations were always born on riversides; it was the ideal location for civilizations. This was due to the abundant availability of water as well as fertile land. Indus Valley Civilization which flourished on the Indus river basin is of great historical value and gave significant contributions to posterity in the way of innovations and other things. The inhabitants of the ancient Indus River valley developed new techniques in handicraft and metallurgy. The Indus cities are noted for their urban planning, baked brick houses, elaborate drainage systems, water supply systems, and clusters of large non-residential buildings.
当你回到地球文明的起源时,所有文明始终诞生在河畔;这是文明的理想位置。这是由于水源和肥沃土地的丰富可得。在印度河流域繁荣的印度河谷文明在创新和其他方面为后人做出了重要贡献。古印度河谷居民发展了新的手工艺和冶金技术。印度城市以其城市规划、烧制砖房屋、精细的排水系统、供水系统和大量非住宅建筑群而闻名。
Among other things, they contain the world's earliest known system of flush toilets. With a number of courtyard houses having both a washing platform and a waste disposal hole. The toilet holes would be flushed by emptying a jar of water, drawn from the house's central well, through a clay brick pipe, and into a shared brick drain, that would feed into an adjacent soak pit (cesspit). The soak pits would be periodically emptied of their solid matter, possibly to be used as fertilizer. Most houses also had private wells. City walls functioned as a barrier against floods. For such good planning, they had to use the river Indus. The urban areas of the Indus Valley civilization provided public and private baths, sewage was disposed through underground drains built with precisely laid bricks, and a sophisticated water management system with numerous reservoirs was established. In the drainage systems, drains from houses were connected to wider public drains.
其中,它们包含世界上已知最早的排水系统。在一些庭院房屋中,有一个洗涤平台和一个废物处理孔。通过从房屋的中央井中取出的水,通过黏土砖管道排入共享的砖排水槽中,进入相邻的浸泡坑(污水坑)中,这些马桶孔将被冲洗。浸泡坑定期清空其固体物质,可能被用作肥料。大多数房屋也有私人井。城墙则起到抵御洪水的障碍作用。由于规划良好,他们不得不使用印度河。印度河谷文明的城市区为公共和私人浴池提供了设施,污水通过精细铺设的砖头地下排水系统进行处理,并建立了多个水库的复杂水管理系统。在排水系统中,房屋的排水管与更广泛的公共排水管相连。
Mohenjo-Daro had more than 700 wells, and most houses had at least one private well. Dholavira had a series of water-storing tanks and step wells, and its water management system has been called "unique". Dholavira had at least five baths, the size of one is comparable with the Great Bath of Mohenjo-Daro.
Wastewater reuse is an ancient practice, which has been applied since the dawn of human history and is connected to the development of sanitation provision. The reuse of untreated municipal wastewater has been practiced for many centuries with the obxtive of diverting human waste outside of urban settlements. Likewise, land application of domestic wastewater is an old and common practice, which has gone through different stages of development.
摩亨佐-达罗有700多个井,大多数房屋至少有一个私人井。多拉维拉有一系列储水槽和台阶式井,其水管理系统被称为“独特”。多拉维拉至少有五个浴池,其中一个的大小可与摩亨佐-达罗的大浴池相比。
废水再利用是一种古老的做法,自人类历史的黎明以来就一直在应用,并与卫生设施的发展相关联。未经处理的市政府污水的再利用已经实践了许多世纪,旨在将人类废物排放到城市之外。同样,家庭污水的土地应用是一种古老而普遍的做法,经历了不同的发展阶段。
Related :What is the Indus Valley civilization?
Short answer about Indus Valley Civilization which i know.
In history, there were four major civilization namely
Mesopotamian
Chinese,
Egyptian
Indus Valley Civilization
Out of which, Indus Valley Civilization is the largest in largest in terms of its area(1,260,000 square kilometres). It was spread over India, Pakistan, Afghanistan etc. Current findings scientists show that the extent of the civilization was even bigger.
关于印度河流域文明的简短回答,根据我所知道的,历史上有四个重要的文明,分别是美索不达米亚、中国、埃及和印度河流域文明。其中,印度河流域文明在面积上是最大的(1,260,000平方公里),它分布在印度、巴基斯坦、阿富汗等地。目前,科学家的研究表明,这个文明的范围甚至更大。
It had Ghagra-Hakra valley to the east, Makran Coast (Baluchistan) to the west, Afghanistan in northeast and Daimabad (Maharashtra) in south.
During its peak, it had a population of 5 million (This is greater than present day population of New Zealand. Most of its inhabitants were artisans and traders.). Out of the 5 million people, many of them lived in villages. archaeologists are having tough time finding culture and society in which they lived because of absence of any proper evidence. Their residences, were made of mud or wood which gets damaged easily and hence no trace is available.
Due to its vast area, 1056 cities have been found. Out of these 1056 cities, 96 of them have been excavated. Dholavaria, Rakhigarhi, Lothal, Kalibangan are some of the famous urban cities apart from Harappa and Mohenjo-Daro.
印度河流域文明的东部有格拉格拉-哈克拉谷,西部有马卡兰海岸(俾路支省),东北部为阿富汗,南部为戴马巴德(马哈拉施特拉邦)。
在其鼎盛时期,该文明有500万人口(这比新西兰现今的人口还多)。大多数居民是手工艺人和商人,而其中许多人住在村庄里。考古学家很难找到他们所生活的文化和社会,因为没有任何确切的证据。他们的住所主要是由泥土或木材建造而成,很容易被损坏,因此没有任何痕迹留下。
由于其广阔的领域,已经发现了1056个城市。其中96个城市已经被挖掘出来。多哈拉维拉、拉基加里、洛塔尔、卡利班甘等著名城市除了哈拉帕和摩亨佐-达罗之外。
Harappans are famous for their world-class drainage system. The usage of flush toilets, removal of waste water, channelling fresh water into bathrooms – they were masters in this area.
Town planning was not limited to cities alone, every town, village and city had the same grid pattern and every house constructed used the same bricks, which were of a particular dimension. The bricks were same for all the houses.
哈拉帕人以他们世界级的排水系统而闻名。使用冲水马桶、排放废水,将清洁的水引入浴室——在这个领域他们是专家。
城镇规划不仅仅局限于城市,每个城镇、村庄和城市都有相同的网格图案,每个建筑所使用的砖块尺寸也相同。这些砖块对于所有房屋来说都是一样的。

Another interesting thing in Indus Valley Civilization is till date there is no evidences of any authority or leader ruling this civilization.
In Lothal, one of the cities of the Civilization, water transport means were available and aquaculture was practised.
These cities had spacious roads. Mohenjo-Daro roads were 10 metres wide and the smallest roads width is estimated to be at least 1.5 m-3m.
The houses used burnt bricks and every house had the same planning (construction) but the rich people had 3 storied houses while the normal ones had 2 storied houses. Those houses had courtyards and terraces too.
印度河流域文明中另一个有趣的事情是,到目前为止没有证据表明有任何权威或领袖统治着这个文明。
在这个文明的一个城市洛塔尔,水运输工具得到了应用,也进行了水产养殖。
这些城市有宽敞的道路。摩亨佐-达罗的道路宽度为10米,最小的道路宽度估计至少为1.5米-3米。
这些房屋使用烧制砖块建造,每个房屋的规划(建设)都相同,但是富人有三层的房子,普通人则有两层的房子。这些房子还有庭院和露台。

Harappa was the first city to be discovered and it was discovered by Dayaram Sahni in 1921. Its present location is in Punjab (Pakistan). It was present on the banks of River Ravi.
The second city to be discovered was Mohenjo-Daro. It was discovered by R.D. Banerjee. Its present location is in Sindh (Pakistan). It was present on the banks of River Indus.The word Mohenjo-Daro literally meant the “mound of dead”.
In Lothal (Gujarat), ruins of dockyard were excavated. Rice was cultivated there and there was a game similar to Chess. People of Indus Valley Civilization traded with Mesopotamian Civilization from there.
哈拉帕是被发现的第一个城市,由达亚拉姆·萨赫尼于1921年发现。它现在位于旁遮普邦(巴基斯坦)。它位于拉维河畔。
第二个被发现的城市是摩亨佐-达罗。它由R.D.班纳吉发现,现在位于信德省(巴基斯坦)。它位于印度河畔。Mohenjo-Daro这个词的字面意思是“死者之丘”。
在古吉拉特邦的洛塔尔,码头的废墟被挖掘出来。在那里种植了大米,还有一种类似于国际象棋的游戏。印度河流域文明人从那里与美索不达米亚文明进行贸易。

In a city called Chanduraho (Indus), evidences of cosmetics were found. Women used lipsticks and other cosmetics. Even small dressing tables were found.
Lets some of their position in early periods.
They were the world’s first dentists.
Earliest scale to test purity of Gold.
The first people to domesticate Cotton.
Indus Valley Civilization people invented the world’s first buttons.
They made the world’s oldest signboard
Another astonishing fact about Induc Valley Civilization is that has surprised the researchers is the absence of any structure which can be thought of central importance like a palace or a temple. The presence of a temple or a palace is a standard feature of every other early civilization. There are several public buildings like the Great Baths and granaries but no structure can be even remotely related to a palace or temple. This has made some scholars to believe that Indus Valley cities were an egalitarian society.
egalitarian means all people are equal.
Yes that’s all i know about Indus Valley Civilization if i get to know anything interesting about Indus Valley Civilization i will upxe.
The best quote which suits for Indus Valley Civilization.
“Civilizations are not remembered by their business people, their bankers or lawyers. They''re remembered by the arts.” - Eli Broad
UPVOTE GUYS IF YOU LIKE MY ANSWER.
THANK YOU!!!
在一个名为钱杜拉霍(印度河流域)的城市,发现了化妆品的证据。女性使用口红和其他化妆品。甚至还发现了小化妆台。
让我们回顾一下他们在早期的一些成就:
他们是世界上第一个牙医。
使用最早的黄金纯度测试比例尺。
第一个驯养棉花的人类。
印度河流域文明人发明了世界上第一个纽扣。
他们制造了世界上最古老的招牌。
印度河流域文明中另一个令研究者惊异的事实是缺乏任何被认为具有中心重要性的结构,如宫殿或寺庙。寺庙或宫殿的存在是每个其他早期文明的标准特征。有若干公共建筑,如巨大的浴池和粮仓,但是没有任何结构与宫殿或寺庙有任何关联。这促使一些学者认为,印度河流域城市是一个平等主义的社会。
平等主义意味着所有人都是平等的。
这是我所知道的关于印度河流域文明的所有内容。如果我了解到关于印度河流域文明的任何有趣信息,我会进行更新。
以下是适用于印度河流域文明的最佳引语:
“文明不是因为他们的商人、银行家或律师而被人们记忆,而是因为他们的艺术。”- Eli Broad
如果您喜欢我的回答,请点赞。谢谢!
All About
= Indus civilization is one of the four earliest civilization of the world along with the civilization of mesopotamia ( tigeris and Euphrates) Egypt (nile) and china ( Hwang Ho ).
= The civilization froms part of the proto-history of india and belong to the Bronze age.
= The most accepted periods is 2500-1700 Bc (by carbon 14 dating).
= Dyaram sahani first discovered harapa in 1921.
= RD Benerjee discovered Mohenjodaro or Mound the dead in1922.
Town planning and structure
= Town planing was not uniform. A common feature was grid systems Street cutting across one another at Right angle, dividing the Town into large rectangle blocks.
= The towns were divided into parts,uper part or lower part.
= Underground drainage system connected all house to the street drains made of moter ,lime and gypsum.They were covered with either brick or stone slabs and equipped with manhole. This shows developed senseof health and sanitation.
= The great Bath it was used for religious bathing. Steps at either end lead to the surface. With inlet to the tank and outlet to drain water . There were changing rooms alongside.
= The Granaries (Harappa)6 granaries in a row were found in the citadel Harappa.
= House were made up of burnt bricks ..
= Lampeter were erected at regular intervals. It indicates the existence of Street lighting.
sonmaninath.blogspot.com
●印度河流域文明是世界上最早的四个文明之一,与美索不达米亚文明(底格里斯和幼发拉底河)、埃及文明(尼罗河)和中国文明(黄河)并列。
●该文明是印度原始史的一部分,属于青铜时代。
●最被接受的时间是公元前2500-1700年(通过碳14测年)。
●Dyaram Sahani于1921年首次发现了哈拉帕。
●RD Benerjee于1922年发现了死人堆或摩亨佐达罗。
城镇规划和结构:
●城镇规划不统一。一个常见特点是网格系统,街道相互交叉成直角,将城镇划分为大矩形区块。
●城镇被划分为上部或下部。
●地下排水系统将所有房屋连接到由灰泥、石灰和石膏制成的街道排水沟。它们覆盖有砖或石板,并配有检修口。这表明他们具有发展健康和卫生意识。
●大浴池是用于宗教沐浴的。两端的台阶通向水面。有进水口和排水口。旁边设有更衣室。
●粮仓(哈拉帕)在城堡哈拉帕发现了6个粮仓。
●房屋由烧制的砖块建造而成。
●灯柱定期竖立。这表明存在街道照明。
来源:http://sonmaninath.blogspot.com/
Sathya Sathesh
By 2600 BCE, small Early Harappan communities had developed into large urban centers. These cities include Harappa, Ganeriwala, and Mohenjo-daro in modern-day Pakistan and Dholavira, Kalibangan, Rakhigarhi, Rupar, and Lothal in modern-day India. In total, more than 1,052 cities and settlements have been found, mainly in the general region of the Indus River and its tributaries.
Mohenjo-daro is thought to have been built in the twenty-sixth century BCE; it became not only the largest city of the Indus Valley Civilization but one of the world’s earliest major urban centers. Located west of the Indus River in the Larkana District, Mohenjo-daro was one of the most sophisticated cities of the period, with advanced engineering and urban planning.
到公元前2600年,小规模的早期哈拉帕社区已经发展成了大型城市中心。这些城市包括今天巴基斯坦的哈拉帕、甘尼隆瓦拉和摩亨佐达罗,以及今天印度的多拉维拉、卡利班甘、拉克希加尔希、鲁帕尔和洛塔尔等。总共发现了1,052个城市和定居点,主要位于印度河及其支流的一般地区。
摩亨佐达罗被认为是建造于公元前26世纪;它不仅成为印度河谷文明最大的城市之一,而且也是世界上最早的重要城市之一。位于拉尔卡纳区的印度河西岸,摩亨佐达罗是该时期最复杂的城市之一,具有先进的工程和城市规划。

Harappa was a fortified city in modern-day Pakistan that is believed to have been home to as many as 23,500 residents living in sculpted houses with flat roofs made of red sand and clay. The city spread over 150 hectares—370 acres—and had fortified administrative and religious centers of the same type used in Mohenjo-daro.
Both cities had similar organization and featured citadels, central areas in a city that were heavily fortified—protected with defensive military structures. Additionally, both cities were situated along the Indus River. This structure would have allowed those at the higher levels of the buildings in either city to look down the river and see into the distance.
哈拉帕是位于今天巴基斯坦的一座有防御工事的城市,据信曾经是居住着多达23,500名居民的地方,他们生活在由红色沙土和黏土制成的雕刻房屋中,并拥有平屋顶。该城市占地150公顷(370英亩),并拥有与摩亨佐达罗相同类型的设有防御措施的行政和宗教中心。
两个城市具有相似的组织结构和特点,都有城堡,即城市中被大量加固、用防御性军事结构保护的中心区域。此外,两个城市都位于印度河沿岸。这种结构使得任一城市楼房处于较高位置的人能够俯瞰河流并看到远处的情况。
The remains of the Indus Valley Civilization cities indicate remarkable organization; there were well-ordered wastewater drainage and trash collection systems and possibly even public baths and granaries, which are storehouses for grain. Most city-dwellers were artisans and merchants grouped together in distinct neighborhoods. The quality of urban planning suggests efficient municipal governments that placed a high priority on hygiene or religious ritual.
Harappans demonstrated advanced architecture with dockyards, granaries, warehouses, brick platforms, and protective walls. These massive walls likely protected the Harappans from floods and may have deterred military conflicts. Unlike Mesopotamia and Ancient Egypt, the inhabitants of the Indus Valley Civilization did not build large, monumental structures. There is no conclusive evidence of palaces or temples—or even of kings, armies, or priests—and the largest structures may be granaries. The city of Mohenjo-daro contains the Great Bath, which may have been a large, public bathing and social area.
印度河流域文明城市的遗迹表明,这个文明的组织极为完善;城市内有井然有序的废水排放和垃圾收集系统,甚至可能还有公共浴室和粮仓,用于储存谷物。大多数城市居民是手工艺人和商人,聚居在不同的社区中。高质量的城市规划意味着高效的市政府,非常注重卫生或者宗教仪式。哈拉帕人展示了先进的建筑技术,包括船坞、粮仓、仓库、砖块平台和保护墙等。这些巨大的墙壁很可能保护哈拉帕人免受洪水袭击,也可能阻止了军事冲突。与两河流域和古埃及不同,印度河流域文明的居民没有建造大规模的纪念性建筑。没有确凿的证据可以证明有宫殿或寺庙,也没有国王、军队或祭司的存在,最大的建筑物可能是粮仓。摩亨佐达罗市包含了一个名为“大浴池”的建筑,可能是一个大型的公共浴场和社交区域。

The people of the Indus River Valley Civilization achieved many notable advances in technology, including great accuracy in their systems and tools for measuring length and mass. Fire-baked bricks—which were uniform in size and moisture-resistant—were important in building baths and sewage structures and are evidence that Harappans were among the first to develop a system of standardized weights and measures. The consistency of brick size across cities also suggests unity across the various urban areas, which is evidence of a broader civilization.
印度河流域文明的人民在技术方面取得了许多显著进展,其中包括他们用于测量长度和质量的系统和工具的高度准确性。经火烤制的砖头是建造浴池和污水结构的重要材料,它们尺寸统一、防潮,也是哈拉帕人最早开发出标准化重量和度量系统的证据之一。不同城市中砖头尺寸的一致性也表明了不同城市之间的统一,这是一个更广泛的文明的证据。

Harappa, Mohenjo-daro, and the recently partially-excavated Rakhigarhi demonstrate the world's first known urban sanitation systems. The ancient Indus systems of sewage and drainage developed and used in cities throughout the Indus region were far more advanced than any found in contemporary urban sites in the Middle East and even more efficient than those in many areas of Pakistan and India today. Individual homes drew water from wells, while wastewater was directed to covered drains on the main streets. Houses opened only to inner courtyards and smaller lanes, and even the smallest homes on the city outskirts were believed to have been connected to the system, further supporting the conclusion that cleanliness was a matter of great importance.
哈拉巴、摩亨佐达罗以及最近部分挖掘的拉基加里展示了世界上已知的第一个城市卫生系统。古印度河流域地区在各个城市中开发和使用的污水和排水系统比现代中东地区的任何城市都要先进得多,甚至比今天巴基斯坦和印度许多地区的城市卫生系统更有效。每户人家都从井中取水,而废水则被引导到主要街道上的覆盖排水沟中。房屋只对内部庭院和小巷开放。即使是城市郊区的最小住宅也被认为与该系统相连,这进一步支持了清洁卫生对于哈拉巴文明来说是非常重要的结论。
Harappans are known for seal carving— the cutting of patterns into the bottom face of a seal, a small, carved obxt used for stamping. They used these distinctive seals for the identification of property and to stamp clay on trade goods. Seals—decorated with animal figures, such as elephants, tigers, and water buffalos—have been one of the most commonly discovered artifacts in Indus Valley cities.
The Indus River Valley Civilization is considered a Bronze Age society; inhabitants of the ancient Indus River Valley developed new techniques in metallurgy—the science of working with copper, bronze, lead, and tin. Harappans also performed intricate handicraft using products made of the semi-precious gemstone Carnelian.
哈拉巴人以刻印章而闻名——在印章的底部刻图案,这是一种小型雕刻物件,用于盖章。他们使用这些独特的印章来识别财产和盖印贸易商品上的黏土。装饰有动物形象(如象、老虎和水牛)的印章是印度河谷城市中最常见的文物之一。
印度河流域文明被认为是青铜时代社会;古印度河谷居民在冶金学领域—即利用铜、青铜、铅和锡进行加工的科学方面开发出新技术。哈拉巴人还使用半宝玉石玛瑙制作精细的手工艺品。

Evidence shows Harappans participated in a vast maritime—sea—trade network extending from Central Asia to the Middle East. The civilization's economy appears to have depended significantly on trade, which was facilitated by major advances in transport technology. The Harappan Civilization may have been the first to use wheeled transport, in the form of oxcarts that are identical to those seen throughout South Asia today. It also appears they built boats and watercraft—a claim supported by archaeological discoveries of a massive, dredged canal, and what is regarded as a docking facility at the coastal city of Lothal. Harappans also engaged in shellworking, and shells used in their crafts have origins from as far away as the coast of modern-day Oman.
证据表明,哈拉巴人参与了从中亚到中东延伸的广泛海上贸易网络。该文明的经济似乎在很大程度上依赖于贸易,而前进的运输技术也促进了这一过程。哈拉巴文明可能是第一个使用车轮运输形式的文明,他们使用耕牛车,这种车辆现在在整个南亚都可以看到。此外,他们还建造了船只和水上交通工具——这一说法得到了考古发现的支持,例如在海滨城市洛塔尔发现的巨大的疏浚运河和被认为是停泊设施的遗址。哈拉巴人还从事贝壳工艺,并且用于其手工艺品中的贝壳来自今天阿曼海岸远至万里之外的地方。
The Indus Valley Civilization declined around 1800 BCE, and scholars debate which factors resulted in the civilization’s demise. One theory suggested that a nomadic, Indo-European tribe called the Aryans invaded and conquered the Indus Valley Civilization, though more recent evidence tends to contradict this claim. Many scholars believe that the collapse of the Indus Valley Civilization was caused by climate change. Some experts believe the drying of the Saraswati River, which began around 1900 BCE, was the main cause for climate change, while others conclude that a great flood struck the area.
印度河谷文明在公元前1800年左右衰落,学者们争论导致这一文明灭亡的因素。一种理论认为,一个名为雅利安人的游牧印欧部落入侵并征服了印度河谷文明,但更近期的证据倾向于否定这一说法。许多学者认为,印度河谷文明的崩溃是由于气候变化引起的。一些专家认为,始于公元前1900年左右的萨拉斯瓦蒂河干涸是气候变化的主要原因,而另一些人则得出结论称该地区遭受了一场大洪水的袭击。
Various elements of the Indus Civilization are found in later cultures, suggesting the civilization did not disappear suddenly due to an invasion. Many scholars argue that changes in river patterns caused the large civilization to break up into smaller communities called late Harappan cultures.Another disastrous change in the Harappan climate might have been eastward-moving monsoons, or winds that bring heavy rains. Monsoons can be both helpful and detrimental to a climate, depending on whether they support or destroy vegetation and agriculture.
后来的文化中发现了印度文明的各种元素,这表明这个文明并没有因为入侵而突然消失。许多学者认为,河流模式的变化导致了大的文明分裂成称为晚期哈拉帕文化的小社区。
哈拉巴气候的另一个灾难性变化可能是向东移动的季风或带来暴雨的风。季风对气候既有益处也有不利之处,这取决于它们是否支持或破坏植被和农业。
By 1800 BCE, the Indus Valley climate grew cooler and drier, and a tectonic event may have diverted or disrupted river systems, which were the lifelines of the Indus Valley Civilization. The Harappans may have migrated toward the Ganges basin in the east, where they could have established villages and isolated farms. These small communities would not have been able to produce the same agricultural surpluses to support large cities. With the reduced production of goods, there would have been a decline in trade with Egypt and Mesopotamia. By around 1700 BCE, most of the Indus Valley Civilization cities had been abandoned.
公元前1800年,印度河谷气候变得更加凉爽和干燥,构造事件可能改道或破坏了河系,而这些河系是印度河谷文明的命脉。哈拉巴人可能向东迁徙到恒河流域,在那里他们可以建立村庄和孤立的农场。这些小社区不可能生产出支持大城市的同样的农业剩余物。随着商品生产的减少,与埃及和美索不达米亚的贸易也将下降。到公元前1700年左右,大多数印度河谷文明城市已经被遗弃了。
The sheer age of the IVC should be interesting to most ordinary people anyway.
So what are the reasons for this neglect??
Some part of neglect is probably due to the Indus scxt being not deciphered till now. Yet, it can be argued that the Linear A scxt is also not deciphered and the culture is still analysed more than IVC.
Does bias and discrimination play the most part here? Is it because that most historians grew up in a Western culture and Western culture shared ideas from the Greek and Roman. So they identified themselves or their ancestors more with the Greek and Roman and so they are more interested in them than IVC?
Or are there any other reasons?
What is the near-term forecast? Will analysis of IVC grow over over a few years or will it remain the same?
印度河谷文明的悠久历史本应引起大多数普通人的兴趣。那么,为什么它会被忽视呢?
部分原因可能是因为迄今为止尚未解读印度文字。然而,可以说线性A文字也没有被解读,但该文化仍然比印度河谷文明被更多地分析。这里是否存在偏见和歧视的因素?是不是因为大多数历史学家在西方文化中成长,并且西方文化分享了希腊和罗马的思想。所以他们对希腊和罗马或者与之有关的先祖更感兴趣,而对印度河谷文明则不太感兴趣?
还是有其他原因吗?未来一段时间内,印度河谷文明的分析会增加还是保持不变?
Trishala
When you travel back to the beginning of civilization on earth, all the civilizations were always born on riversides; it was the ideal location for civilizations. This was due to the abundant availability of water as well as fertile land. Indus Valley Civilization which flourished on the Indus river basin is of great historical value and gave significant contributions to posterity in the way of innovations and other things. The inhabitants of the ancient Indus River valley developed new techniques in handicraft and metallurgy. The Indus cities are noted for their urban planning, baked brick houses, elaborate drainage systems, water supply systems, and clusters of large non-residential buildings.
当你回到地球文明的起源时,所有文明始终诞生在河畔;这是文明的理想位置。这是由于水源和肥沃土地的丰富可得。在印度河流域繁荣的印度河谷文明在创新和其他方面为后人做出了重要贡献。古印度河谷居民发展了新的手工艺和冶金技术。印度城市以其城市规划、烧制砖房屋、精细的排水系统、供水系统和大量非住宅建筑群而闻名。
Among other things, they contain the world's earliest known system of flush toilets. With a number of courtyard houses having both a washing platform and a waste disposal hole. The toilet holes would be flushed by emptying a jar of water, drawn from the house's central well, through a clay brick pipe, and into a shared brick drain, that would feed into an adjacent soak pit (cesspit). The soak pits would be periodically emptied of their solid matter, possibly to be used as fertilizer. Most houses also had private wells. City walls functioned as a barrier against floods. For such good planning, they had to use the river Indus. The urban areas of the Indus Valley civilization provided public and private baths, sewage was disposed through underground drains built with precisely laid bricks, and a sophisticated water management system with numerous reservoirs was established. In the drainage systems, drains from houses were connected to wider public drains.
其中,它们包含世界上已知最早的排水系统。在一些庭院房屋中,有一个洗涤平台和一个废物处理孔。通过从房屋的中央井中取出的水,通过黏土砖管道排入共享的砖排水槽中,进入相邻的浸泡坑(污水坑)中,这些马桶孔将被冲洗。浸泡坑定期清空其固体物质,可能被用作肥料。大多数房屋也有私人井。城墙则起到抵御洪水的障碍作用。由于规划良好,他们不得不使用印度河。印度河谷文明的城市区为公共和私人浴池提供了设施,污水通过精细铺设的砖头地下排水系统进行处理,并建立了多个水库的复杂水管理系统。在排水系统中,房屋的排水管与更广泛的公共排水管相连。
Mohenjo-Daro had more than 700 wells, and most houses had at least one private well. Dholavira had a series of water-storing tanks and step wells, and its water management system has been called "unique". Dholavira had at least five baths, the size of one is comparable with the Great Bath of Mohenjo-Daro.
Wastewater reuse is an ancient practice, which has been applied since the dawn of human history and is connected to the development of sanitation provision. The reuse of untreated municipal wastewater has been practiced for many centuries with the obxtive of diverting human waste outside of urban settlements. Likewise, land application of domestic wastewater is an old and common practice, which has gone through different stages of development.
摩亨佐-达罗有700多个井,大多数房屋至少有一个私人井。多拉维拉有一系列储水槽和台阶式井,其水管理系统被称为“独特”。多拉维拉至少有五个浴池,其中一个的大小可与摩亨佐-达罗的大浴池相比。
废水再利用是一种古老的做法,自人类历史的黎明以来就一直在应用,并与卫生设施的发展相关联。未经处理的市政府污水的再利用已经实践了许多世纪,旨在将人类废物排放到城市之外。同样,家庭污水的土地应用是一种古老而普遍的做法,经历了不同的发展阶段。